Trading in any of the capital markets involves buying and selling. Although, the prices for buying and selling the same instrument are mostly different. This difference between the bid and ask price or buy and sell price is called the spread.
The spread plays a major role in forex trading as it is the primary source of earning for the forex brokers. Most of the forex brokers charge variable or floating spreads but some of them also offer fixed spread accounts.
Spreads can also single-handedly influence the profits or loss made by the trader. This article covers all the details of the spreads you should know before trading in forex markets.
In the simplest definition, spread is the difference between the bid and ask price of the currency pair.
Every time you check the prices of any currency pair, you can see 2 different prices for each currency pair. The first price i.e. lower price is the selling price or ask price while the higher price is the buying or bid price. The difference between the buying and selling price of the currency pair is called as spread.
Generally, the difference in the bid and ask price of a currency pair is only visible on the fourth decimal. Hence, the spread is commonly depicted as an integer that denotes the difference on the fourth decimal point of the bid and ask price.
The spreads are denoted by percentage in points (pips). 1 pip is the difference between the fourth decimal points of buying and selling price of the currency pair.
It is the main source of income for the forex brokers who do not charge any commission. When you buy a currency pair you pay a slightly higher price than the price at which the broker is buying the currency pair for you.
Similarly, the broker sells at a slightly lower price than the price at which you are selling the currency pair. The extent to which this gap differs depends entirely upon the spread.
If the spread is 0 pips, then the buy price and the selling price will be the same. In such a case, the broker will not be able to make any profit if the clients execute trades. Such brokers may charge a commission on each trade to make profits.
Spread in forex trading and its effect on profit or loss can be better understood with the help of an example.
The role of spread & it’s calculation can be better understood with the help of an example. In this example, we will also try to understand the effect of spreads on profits and loss while trading in forex.
We have taken EUR/USD as a reference currency pair.
It is important to understand that by trading on EUR/USD currency pair, you are buying/selling the predefined lots of the Euro by exchanging the USD.
Suppose, the EUR/USD is trading at 1.80018/1.80000. The spread, in this case, is 1.8 pips i.e. difference in the fourth unit of bid and ask price.
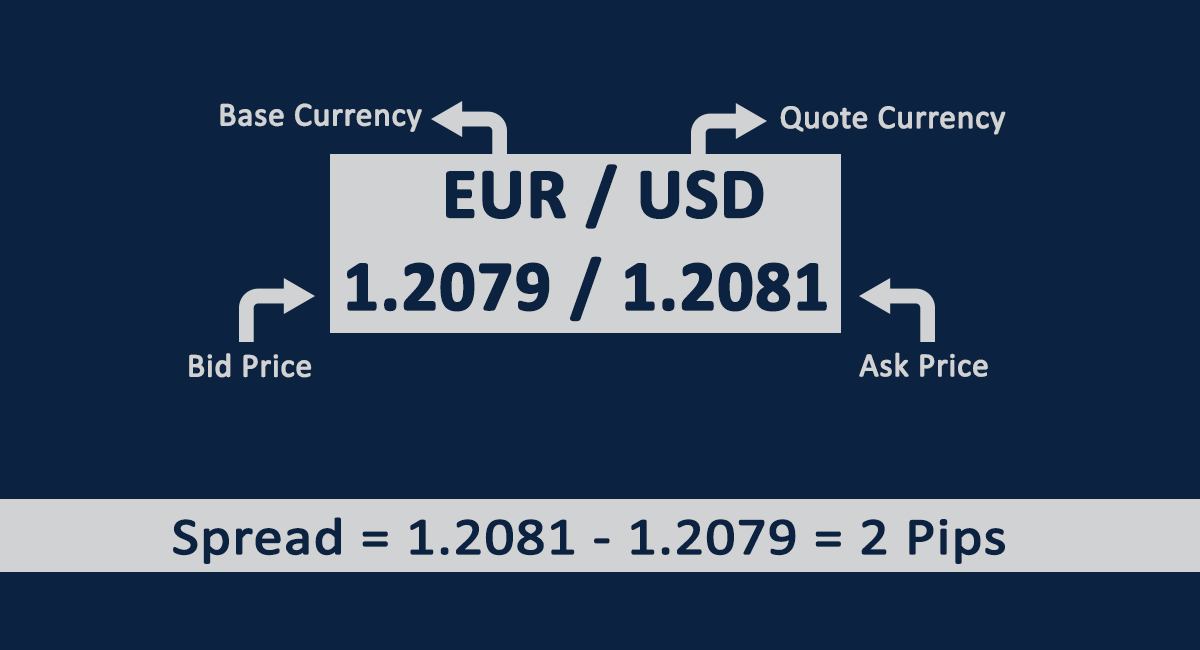
In this example, the bid price or buying price of EUR/USD currency pair is 1.80018.
This means that if a trader desires to go long on EUR/USD, he will have to pay 1.80018 USD to buy 1 unit of EUR. Forex trades are executed in lots. A standard lot contains 100,000 units of the quote currency.
If the trader feels that the price will drop, he will sell the specified lots of EUR/USD at 1.80000 per unit. The selling price is always lower than the buying price for any currency pair unless the broker is offering 0 spreads on forex pairs.
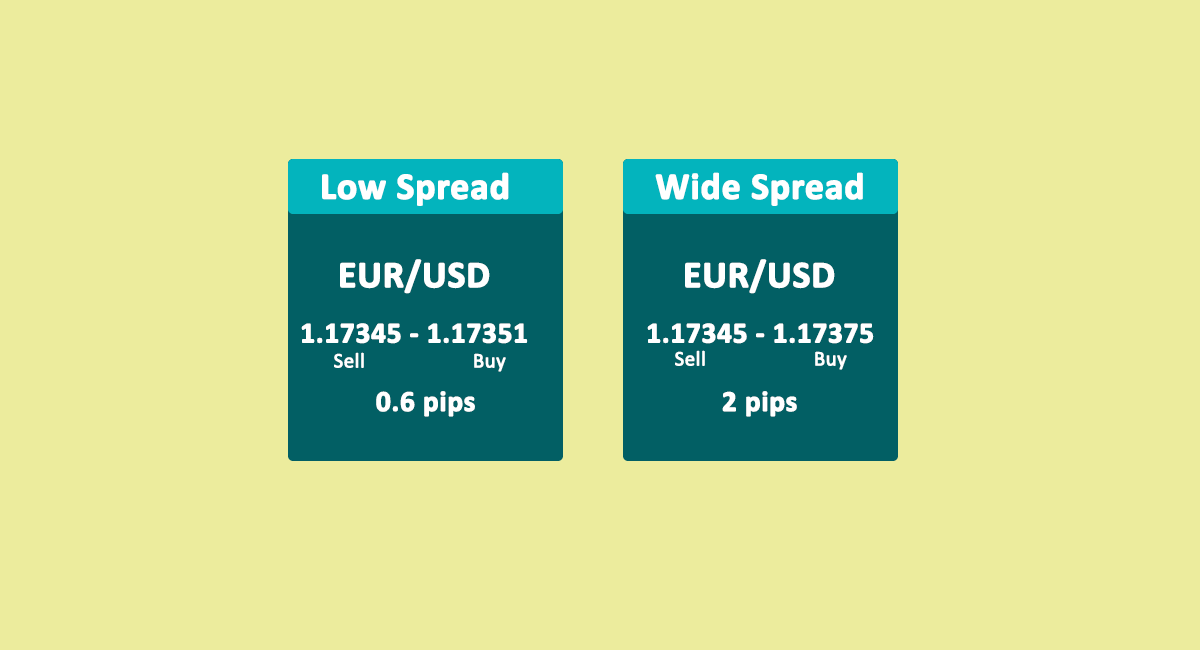
It can be noted that to book profits on both the side of the trade, the price needs to change more than the spread. Hence, there is a lesser probability to book profit if the spread is wider. Profits can be booked easily if the spreads are narrower.
If the price moves against the prospect, traders will face losses by the extent of price movement added by the spreads.
Suppose you placed a buy order on EUR/USD at 1.180018 when the selling price was 1.180000 units of the base currency. After few minutes, the selling price dropped to 1.170990. If the trader closes the position, he will face a loss of 0.00028 per unit. It must be noted that the selling price only dropped by 0.00010 but the spread is 1.8 pips per lot which will be added to the overall loss.
Spreads can largely affect the overall gains/losses from forex trades. All the charges incurred while executing a trade are included in the spread.
The spreads can differ from broker to broker for the same currency pair. Many brokers offer multiple account types and charge different spreads with each account type.
A forex broker doesn’t need to offer all types of spread. Majority of regulated forex brokers in the world charge variable spreads on currency pairs.
The floating spreads can change differently for different liquidity providers in forex trading.
The spreads can widen or increase whenever there is an effective announcement that can potentially fluctuate the prices of currency pairs. Floating spreads can widen dramatically when the markets are volatile or liquidity is low.
The spreads generally tend to get narrower when the markets are stable, liquidity is high, and no major economic event is expected to take place in the near future.
The spreads need to fluctuate depending upon market conditions. Wider spread during stable markets will reduce profit-making opportunities and can reduce the number of traders that will eventually reduce liquidity. Low spreads during volatile markets won’t be good for the brokers and might include requotes.
The fluctuations in spreads can be dramatic at times. There are multiple reasons that can affect the spreads of every currency pair. The variable spreads can be different for each forex broker as the liquidity provider can be different for each broker.
Lower spreads will not only increase the probability of booking profit but can also increase the amount of profit. Traders will face lesser loss if the spreads are lower.
Lower spreads will always be beneficial for the forex traders. Although, paying a high commission in return for a lower spread might not be a right decision for the new or low volume traders.
It is always advisable to check and compare the spreads offered by different forex brokers before choosing any.
2021's Best FX Brokers
See Rank